Send large files
With Cryptshare you can send files of any size.
Any type directly from your email program.

How to make your data transfers quick and easy
- while respecting data protection.
In everyday business, large files cannot be sent as email attachments (between sender and recipient). Our solution takes care of exactly these digital logistics.
With Cryptshare you can send files of any size and any type directly from your email program. This is simple, secure and saves valuable time! Your contact partners can also use Cryptshare to send files back to you - without costs or extra effort.
File too big for an email attachment yet again?
We’ve all been there. After all, many email clients only allow for sending files up to 20 megabytes – given today's data volumes, that is not nearly enough. So what can you do? Users often resort to stopgap solutions they are familiar with, such as WhatsApp or Dropbox – a real nightmare for corporate compliance.
But that doesn't have to happen because there is a simple and secure solution: Cryptshare! With Cryptshare, you can not only send large files, but also do so in a way that is compliant with data protection. And what’s more:
Cryptshare is super easy to use – if you can use email, you can use Cryptshare. This makes both users and admins happy! It’s simple: write a message, insert files via drag & drop, and click send. That's it!
Want it to be even more convenient? There are integrations for Outlook and HCL Notes. And if you want to boost digitalisation in your enterprise and connect an in-house tool, you can do so with the Cryptshare API. You take care of your work, and Cryptshare will take care of the digital logistics.
Just so you know: Cryptshare works bidirectionally, which means that all of your contact partners can also send messages and files back to you securely and confidentially - without additional costs, training or further effort. To learn more about how to enable secure digital communication for your entire workforce, try Cryptshare or ask us for a consultation!
- Intuitively to use
- Send files of any size
- Encrypted file transfer
- No user accounts needed
- Malware protection and file type filter
- Automated deletion of all files on server
- Integrated into Outlook
- Integrated into HCL Notes
- Automated file transfers
Large files and data transfers in companies and organisations
Requirements for file transfers are constantly increasing:
In the modern business world, sending data is a regular part of everyday work - and will become even more important in the future. It is important for every organisation to enable its staff to transfer large files of several GB and to meet the following requirements in particular:
Data protection requirements
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation has been applicable law since the end of May 2018. With the aim of protecting personal data and ensuring the free exchange of data within the EU, it includes important rules that must be complied with - otherwise there is the threat of severe penalties:
In accordance with paragraph 2, fines of up to EUR 20,000,000 or, in the case of a company, up to 4 % of the total annual worldwide turnover in the preceding business year, whichever is higher [...].
GDPR Art. 83 (5)
What is equally important, however, is that the GDPR also applies to data concerning EU citizens that is sent abroad from the area of application of the GDPR. This is because the data must be subject to at least the same level of protection there as is legally ensured by the GDPR. Today, files are increasingly stored in the cloud and the largest providers of such services are located in the USA. This means that many data flows of companies and organisations are affected, which they are not even aware of at first. Files are often not consciously sent to the USA, but flow there in the background. Nevertheless, European organisations can be held liable for violations, especially since legal foundations such as the Privacy Shield were overturned by the European Court of Justice.
For companies as well as organisations, it is therefore important to always guarantee the prescribed data protection and to also ensure compliance with the GDPR when transferring large files.
Internal policies:
Companies and organisations often have internal guidelines concerning the sending of files. These also contain concrete guidelines on how to handle incoming and outgoing data and how to store them. For example, if an archiving system is connected. In this case, internal regulations determine what is stored, how and where.
Admins also like to use file type filters as a security measure to ensure compliance with internal guidelines. With these, they can ensure that only the file types they have defined as trustworthy are allowed and others are blocked. Such filters are mainly used when certain types of files are frequently used for malware attacks.
Protection against access by unauthorised third parties
What is already important for compliance with the GDPR for personal information also comes into play for data concerning one's own organisation - when protecting one's own intellectual property. It is not uncommon for large files of several GB, often with content worthy of protection such as patent applications or construction plans, to be sent electronically. To prevent industrial espionage or hacking attacks, it is necessary to protect such data in the transfer from sender to recipient(s) through effective encryption.
User-friendliness
This is one of the most important requirements for any software solution but is all too seldom given sufficient focus. Ultimately, however, it is user-friendliness that determines whether a solution for secure data transfer is used in practice. If such a solution is too cumbersome or complicated for the staff, it will not be used in everyday work - no matter how technically sophisticated it may be. It is crucial that the solution can be used quickly and easily by all employees and that it works without much training. Simple rollout, simple integration into existing work processes, simple handling: this is what makes users and admins happy!
Data volumes are growing rapidly - how large files are created:
Data has enormous importance across industries and needs protection in different gradations. With powerful software, employees create large files of several gigabytes every day, e.g. with Microsoft Office programs such as PowerPoint and Excel, with databases and through CAD files, videos or pdfs. With new technologies, the quality of data sets is increasing - and so is the amount of data, file size and storage space required for them.
Data unfold their true value when they are shared with others and can thus be worked with. For example, when even large files such as an MRI scan can be sent quickly and easily to a specialist to obtain a second expert opinion. What is important here is that such transfers are secure and data protection compliant through encryption. Your workforce wants to work with files in different locations and devices, and many of the recipients with whom they share data are outside your organisation. So how can file transfers be made secure and privacy compliant? After all, such transfers involve important and confidential aspects of your business.
It was not so long ago that physical media were used to transfer such data. On these, the information was stored and then shared with the recipients. In the end, however, DVD, USB stick and co. could not keep up with developments and became increasingly impractical for the transfer of large files in particular, especially in the business sector.
There were good reasons for this:
- The size limit of the data carriers, which could not keep up with the maximum file sizes indefinitely: The available storage space was then simply no longer sufficient.
- The postage costs for shipping: Especially in total, considerable sums could quickly arise.
- A lot of shadow IT was created and data sovereignty was lost very quickly: it simply became impossible to track how many data sets were on the move and where.
- For malware, physical data carriers are a gateway that hackers like to use: where it is common to work with USB sticks, the threshold for their use is quite low. It is sometimes sufficient to label a suitably prepared data carrier with "employee salary list" or similar, to deposit it in a company car park or even to drop it by drone. If just one member of staff cannot resist curiosity and plugs the stick into their computer at work, the integrity of IT within the organisation is over.
Nowadays it is common to send large files digitally. This is faster, easier and saves money. But there are also many pitfalls to be aware of.
How large files are usually sent digitally:
The corporate approach
To make these decisions, people often narrow their view too much; they then take a closer look at complex and costly tools like SMIME or less secure solutions like in-house FTP servers. Standard email and cloud solutions such as Dropbox or Gmail are also often chosen as the fastest way to share any file at any time.
Cloud services are popular especially when there is a requirement for a large amount of storage space, but these are not always the most sensible solution. For many organisations, it is important to retain data sovereignty and to be able to guarantee that no data flows in the background to the large cloud providers in the USA. However, due to the US-CLOUD Act of 2018, it is not enough if the server with the relevant data is located in Germany; as long as the parent company is American, US authorities still have access rights to the data. This also affects some providers of secure communication, such as WeTransfer. Although this company is based in the Netherlands, it also uses servers in the USA for its cloud, where data from users' transfers is stored. US authorities therefore also have access to this data in principle. In order to prevent this and ensure data protection at the GDPR level, EU companies with servers in the EU are needed. IT decision-makers in companies and organisations must be absolutely clear about this point!
Data storage in the USA is not subject to such a strict legal framework as in the European Union. Although there is the California Consumer Protection Act (CCPA) in California, which gives consumers more rights over the use of their data, it is still in a pioneering role and is only bindingly in force in the state of California. While in this country data protection for those affected is the focus, in the USA commercial interests are given greater consideration. Therefore, data transfer to third parties without the explicit consent of the data subjects is common practice there in many industries, whereas this is prohibited in the EU by the GDPR. In principle, companies and organisations in the US have much more discretion than their European counterparts as to how strong their data protection should be. In shaping this leeway, the high commercial value of the data is therefore very high on the list of priorities.
Both the legal requirements for data storage and data handling are fundamentally different in the EU than in the US. Companies in the area covered by the GDPR must therefore keep a close eye on where their data goes - especially when it comes to sending large files.
Sometimes companies and organisations already have solutions and services in place to send or receive data. At the same time, however, they are often not used and the workforce switches to applications that they are familiar with from their private lives. These are usually not GDPR-compliant and have not been approved by the in-house IT. The resulting shadow IT therefore causes nightmares for the admins, because they have no knowledge of which data of their company or organisation is circulating where. However, shadow IT does not only occur when there is no solution for the secure exchange of data; it is already enough if the users find the solution too cumbersome or complicated to use.
Once workarounds have become ingrained in the daily work routine of the staff, it is difficult to get rid of them again. It is therefore all the more important that organisations prevent such workarounds from the outset by providing their staff as early as possible not only with a communication solution that is secure and compliant with data protection requirements, but also one that can be easily used by all employees.
In the everyday work of the workforce
There are many ways to send large files of several GB from the sender to the recipient's side. Employees are familiar with many providers of such services from their private lives, such as DropBox, WhatsApp, OwnCloud or WeTransfer. But this is exactly what can become a problem for any organisation.
Especially solutions from the consumer sector are not suitable for sending data that is subject to external or internal compliance requirements. They do not always use encryption and the transport route over which the data is sent is not necessarily protected from access by unauthorised third parties. Moreover, such solutions undermine the data sovereignty of organisations. Dropbox, WhatsApp, WeTransfer and the like are quickly used, but leave the IT department completely in the dark about what data flows out when and where.
Nevertheless, employees like to use such solutions as a workaround. Why? It is true that many users are unaware of the catastrophic consequences for their own organisation of "just quickly" sending large files via unauthorised channels when they use them all the time in their private lives anyway. Even more serious, however, is the fact that services for private use are just that: "simple" and "fast", especially in use. In the case of doubt, this usually trumps any security concerns.
Even if companies have provided approved options for securely sending large files, these are often avoided and bypassed by the workforce. This circumstance is also closely related to the high user-friendliness of the offers and their familiarity from the private sector.
Conclusion for organisations and companies:
The security of solutions for sending large files must therefore by no means be at the expense of user-friendliness!
Experience shows: If your organisation does not provide a solution that is easy for your staff to use, they will be tempted to find workarounds. As a rule, they then use old familiar - and unapproved - means over which your IT has no influence.
Sending large files with Outlook
Remove file size limit for email attachments in Outlook
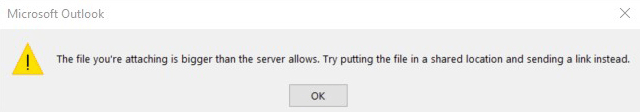
Microsoft Outlook Warning: The file you´re attaching is bigger than the server allows. Try putting the file in a shared location and sending a link instead.
From time to time, most users need to send large files with Outlook.
When you try to send a large email in Outlook, you are faced with two file size limitations:
- The file size limit set by the mail server of your email recipient
- The file size limits set by your Outlook itself.
Outlook limits the size of email attachments to a total of 20 MB. It makes no difference whether a single file with 20 MB or several smaller files are attached;
If the total size of the email attachment exceeds 20 MB, a warning message will appear that is well-known by most Outlook users:
Problems with large email attachments
Now one could certainly discuss whether one can still speak of a "large file" at 20 MB nowadays. Furthermore, this file size limit for email attachments dates back to the previous millennium.
Nevertheless, these restrictions give legitimate hints to problems resulting from large email attachments, no matter if with or without Outlook:
- Large emails (or emails with large attachments) cause your email recipients' storage quotas to become very busy
- Large attachments also burden your own email storage quota (for example, Exchange) by storing the data in the Sent Items folder.
If you then add yourself, or perhaps work colleagues, to CC/BCC, the memory consumption can increase many times over again.
Send large files in Outlook - With Cryptshare
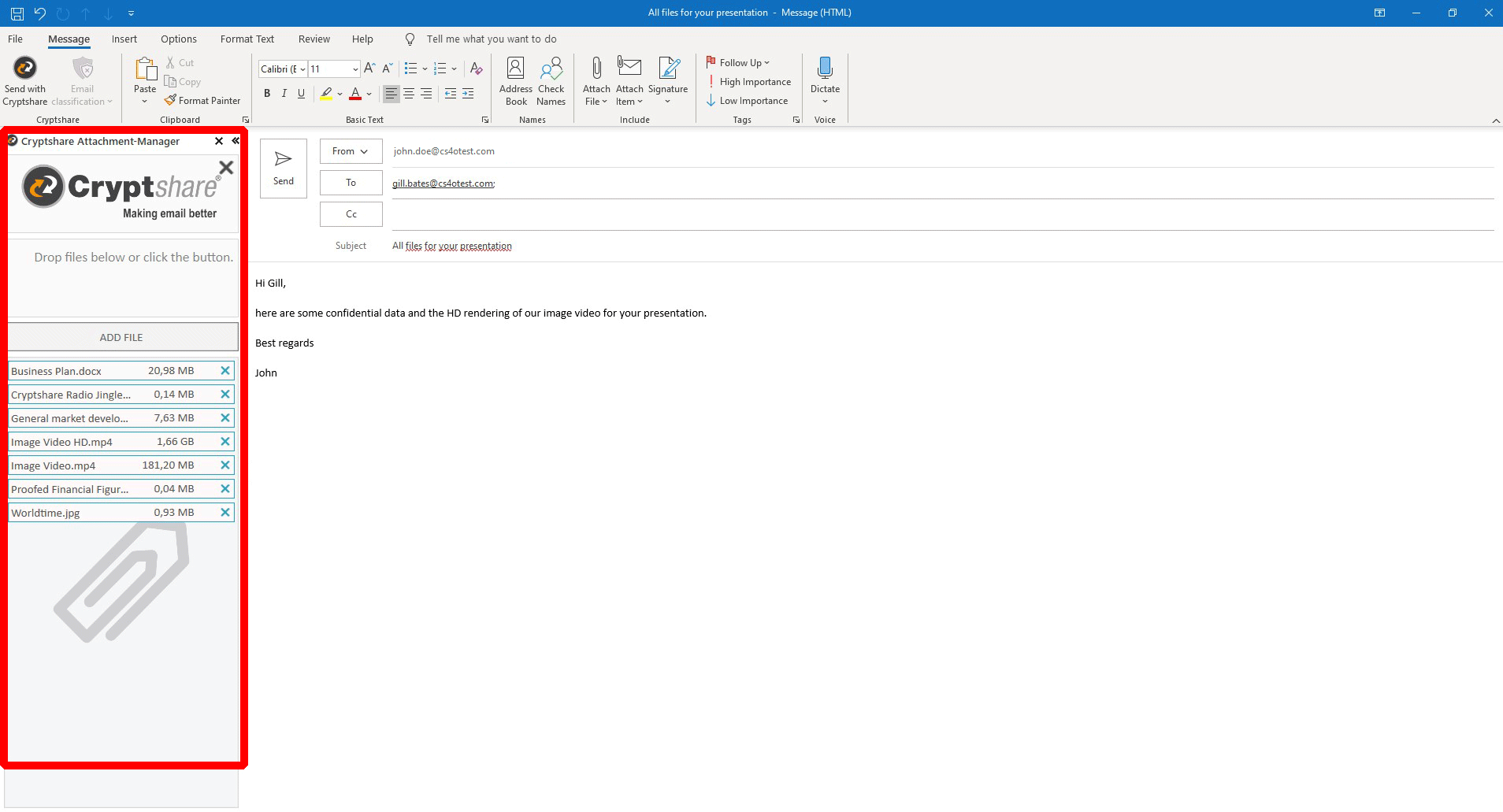
With our Outlook add-in "Cryptshare for Outlook", you can create your emails in Outlook as you are used to.
It extends Outlooks capabilities so you can attach very large files to your message, up to multiple gigabyte.
You don't have to take care about attachment file size limitations in Outlook anymore! The Cryptshare Attachment-Manager will be activated automatically, when the total attachment file size exceeds a previously defined threshold (5 MB by default).
The files are then not transported via email anymore, but via your Cryptshare server. Even taking the load off your and the recipient's email system. Only your system administrator can limit the size by configuration.
Please note:
We recommend, to watch our video (File attachment handling starts at 1:05) to see how easy it is to send large files in Outlook with Cryptshare.
With our Outlook Add-In Cryptshare for Outlook you can create your emails in Outlook the way you are used to.
It extends the possibilities of Outlook in that you can attach very large files to your message, up to several terabytes.
You no longer have to worry about the size limits for attached files in Outlook! The Cryptshare Attachment Manager is automatically activated when the total file size of the attachment exceeds a predefined threshold (5 MB by default).
The files are then no longer transported by email but via your Cryptshare server.
This even relieves the load on your email system and that of the recipient. Only your system administrator can limit the size by configuration.
Sending large files with the Web App
Upload and share large files via browser
The Cryptshare Web App is the central point of communication and can be used at any time from any PC, tablet or smartphone.
All you and your external communication partners need to exchange confidential data or large files is a browser and an email address.
The Cryptshare Web App is self-explanatory and intuitive to use - the user is guided step by step through the transfer process. No training or support is necessary.
Sending large files via HCL Notes
Remove file size limit for email attachments in HCL Notes
With our HCL Notes integration Cryptshare for Notes you can attach files of any size to your emails and send them securely.
File transfer methods and their Pros and Cons
Removable Media
Easily lost or stolen. Very likely to turn up during waste disposal.
Whilst the cost of mass storage has fallen dramatically widespread use of removable media adds up. USB sticks are more expensive than CD and used widely across organisations, as is common leads to a significant cost.
Not a day passes without lurid details of security breaches where a USB stick or CD is left on a train, recovered from a dustbin or dropped in the street. Once the data is on these devices it tends to stay there. To test this look in your desk drawer, do you find any USB sticks? Now take a look and see if there is anything confidential on them…
Removable media gets lost and stolen, and it gets recycled. Even when encrypted it remains a material risk to data security and in many companies it is prohibited. It remains one of the most frequent cause of data breaches.
Very easy to use, very easy to loose.
Cloud Services
Consumer grade. Places your most sensitive data outside into the "Wild West".
On the face of it very low until you dig into to it to find out who is expensing the drop box accounts. Suddenly it looks expensive, and the risk of compliance breach is very, very high.
Poor, in general the cloud solution vendors are fighting hard to defend private data but stories of breaches are frequent. In addition issues such as data location and legal jurisdiction are becoming new vectors for data loss or breach.
These services are used in an ad how and uncontrolled manner and so do not fit the governance requirements of an organization. Breaches when they occur cannot be defended.
Ease of use – These are appealing and easy to use solutions. They are a low stress choice for individuals and a high risk and complex problem for the organization to unravel.
FTP
Requires management of user accounts and may be a graveyard for data.
Once set up and running an FTP server is relatively cheap to run but they will most often occupy a member of your staff for some time to build and manage. Transaction costs are low but access may be complicated so user set-up and support will take time.
In house FTP servers are not secure. User access controls are frequently rudimentary and it is common to find large amounts of legacy data on older ftp servers which have not been purged, however they have the benefit of being inside your DMZ.
Large files may be handled by ftp servers, but controlled availability data integrity and user authentication are weaknesses and the concepts of non-repudiation are handled poorly. Some level of audit trail is possible.
For non-technical users ftp services are un-popular and with security being especially low outside the DMZ services based on ftp are sporadic in use. However relative ease of access and lower authentication hurdles mean that they are easy to use.
Secure FTP
Complex to use, time-consuming to set up and operate. May conflict with other infrastructure.
More expensive than regular FTP and more complex to install and create SFTP can place a very large burden on your corporate IT infrastructure and on IT staff to install administer and manage. The need for user accounts and administration add to the costs.
Bringing encryption in transit and in storage provides short term security but often poor long term management of the data store. SFTP does have the benefit of running inside the firewall and being locally administered offers some configurability. In the long term SFTP solutions tend to be updated infrequently and are vulnerable to current threats.
SFTP services are rarely certified but they have some advantages, high security, clear process inclusion often policy driven and a clear audit trail. Against this is the problem of ad hoc usage and management which can place barriers to use.
Requiring a client installation SFTP takes time to set up and some level of training before it can be used. For the client end it is more complex to use than SFTP and policy creation is complex. Back to overview Learn now how to transfer files using Cryptshare.
MFT Solutions
Secure but complex. Limited for ad-hoc requirements. Expensive.
Whilst offering comprehensive functionality these solutions are very expensive to licence to install and to manage. Because of their complexity they also create barriers to use, require training and often require external users are licenced.
Is high, encryption is strong if complicated to use multiple policy tools and options allow strong control. In general these products are designed towards narrow security functional requirements with the addition of features later on. Complexity may put some users off.
Good governance depends on use and if complexity or high cost, slow implementation or technical barriers intrude this is placed at risk. The products have the ability to offer high levels of good governance at a price, but they possess a downside risk.
Very wide functional capability mitigates against ease of use. Once mastered then always used but to truly gain the best of these tools extensive training is mandatory. Training introduces cost and time in implementation.
Post and courier Services
Still perceived as safe, but old-fashioned, slow and expensive.
Very expensive for each and every use and very slow by comparison to electronic communications. There is a $50bn per annum business shipping A4 sized envelopes around the world.
Good, documents are packaged and cannot be read and in general loss rates of documents are very low. The records of most modern logistics companies are excellent in maintaining security, breaches typically occur before shipping and after delivery.
Whilst use of courier services in very well established in certain markets many companies are seeking faster and cheaper ways to share documents with less impact on the environment.
Easy to use, but most often used by third parties, PA’s and secretaries. Ease of use tempered by very slow speed of delivery and return.
FAQ about large file transfers
How to send large PowerPoint files?
Large PowerPoint presentation files in marketing
The presentation software PowerPoint has been established in the business world for decades. Admittedly, there are established alternatives such as Prezi, Keynote, Google Slides or Impress from LibreOffice. However, PowerPoint is firmly established in the broad desktop environment. Since the topic of "creating appealing presentations" is traditionally located in the marketing department, presentations are correspondingly frequently edited there.
When are PowerPoint presentations sent out?
The content of presentations is often still prepared in the specialist departments such as sales and development or at management level. However, the PPTX documents are then usually handed over to the marketing department to be prepared in line with corporate design or "to make them look good". Before larger events, in the "hot phase", it can also happen that several departments prepare their slides simultaneously and independently and send these individual slides to Marketing.
This happens partly via releases in the file system, but often also by email. However, PowerPoint documents very quickly exceed the file size of 25 MB. Above this data volume, however, email servers often no longer accept incoming emails. At that point, employees often get creative and look for their own ways to deliver the PowerPoint files to marketing, not infrequently using unauthorised, free cloud services they know from their private lives.
Why are PowerPoint presentations often so large?
PowerPoint presentations go far beyond mere collections of texts, tables, graphics and screenshots. They have long since evolved into genuine multimedia presentations and contain embedded video files (avi,mp4), audio files (wav,MP3) and other documents such as PDF. All too often, all kinds of media are carelessly inserted in the design phase without considering the file size of the individual media. However, before integrating them into the presentation, they should be prepared by an experienced media designer in a media-friendly way, i.e. scaled down, cut and compressed in the correct file format. In this way, the file size can be drastically reduced and you retain the best possible ratio of image/sound quality and data volume.
Why free cloud providers are often a bad choice
When you send large PowerPoint files via free cloud providers, the ownership rights often pass to the provider. The transfer size is limited, the data is not encrypted and you can no longer recall uploaded PowerPoint presentations if you have entered the wrong email address as the recipient.
It is better to send your PowerPoint file online via your own server, for example with our solutions for secure data exchange.
How to send large videos?
Large videos in Marketing
In the age of video marketing, marketing departments are involved in the production of video campaigns on a daily basis.
After the first video was uploaded to YouTube in 2005, numerous other video channels such as TikTok, Twitch and GIPHY have since been established. In LinkedIn, Facebook and Twitter, too, reach and interaction rates can be significantly increased through entertaining video content.
Accordingly, marketing staff produce, edit, compress and send videos of various sizes, depending on the requirements of the channel and the end devices.
Why are video files often so large?
Due to ever-improving playback devices and displays, the file size of videos is increasing analogue to the resolution from SD with 858x480 pixels to HD with 1,280x720 pixels or Full HD with 1,920x1,080 pixels up to 4K with 4,096x2,160 pixels. Thus, a high-resolution video with a high frame rate reaches several GB per minute.
The challenges of sending large videos
Sending these large video files to customers, partners and suppliers can be a challenge; during the production phase of a video, agencies and marketing departments often still use the cloud services of the video editing software to collaborate on it, for example, after previewing a rough cut. However, when the final rendering is then available in the file system and needs to be sent "once again quickly" to external recipients, free cloud providers such as WeTransfer or Dropbox are often used. Simply because there is no in-house solution that is adapted to the company's own needs.
Why free cloud providers are often a bad choice
When you send large videos via free cloud providers, the ownership rights often pass to the provider. The transfer size is limited, the data is not encrypted and you can no longer recall uploaded videos if you have entered the wrong email address as the recipient.
It is better to send your videos online via your own server, for example with our solutions for large file transfers.